Ticks and their control » książka
Ticks and their control
ISBN-13: 9786206844679 / Angielski / Miękka / 252 str.
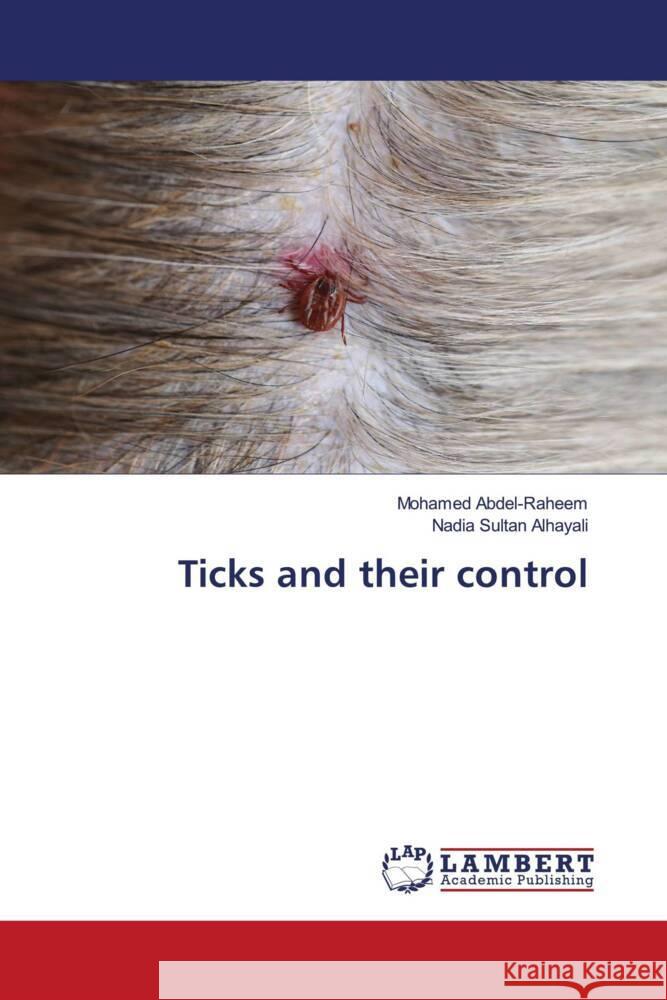
Ticks are able to transmit tick-borne infectious agents to vertebrate hosts which cause major constraints to public and livestock health. The costs associated with mortality, relapse, treatments, and decreased production yields are economically significant. Ticks adapted to a hematophagous existence after the vertebrate hemostatic system evolved into a multi-layered defense system against foreign invasion (pathogens and ectoparasites), blood loss, and immune responses. Subsequently, ticks evolved by developing an ability to suppress the vertebrate host immune system with a devastating impact particularly for exotic and crossbred cattle. Host genetics defines the immune responsiveness against ticks and tick-borne pathogens. Pesticides are commonly regarded as substances used to control organisms such as insects, fungi, weeds, and microbes that destroy plants, particularly those for food production. EPF are a species of fungal pathogens for arthropods. They are considered cosmopolitan saprophytic organisms that live in diverse ecosystems and climates (e.g., tropical, temperate, arid and artic), where they interact with arthropods in many terrestrial and aquatic habitats.