topmenu
Wyniki wyszukiwania:
wyszukanych pozycji: 11
 |
Fluoretos e fluorose não esquelética
ISBN: 9786208355517 / Portugalski / Miękka / 2024 / 104 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. |
cena:
275,95 |
 |
Fluoruri e fluorosi non scheletrica
ISBN: 9786208355500 / Włoski / Miękka / 2024 / 104 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. |
cena:
275,95 |
 |
Inter-relação periodontal e sistémica
ISBN: 9786208321932 / Portugalski / Miękka / 2024 / 100 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. |
cena:
271,70 |
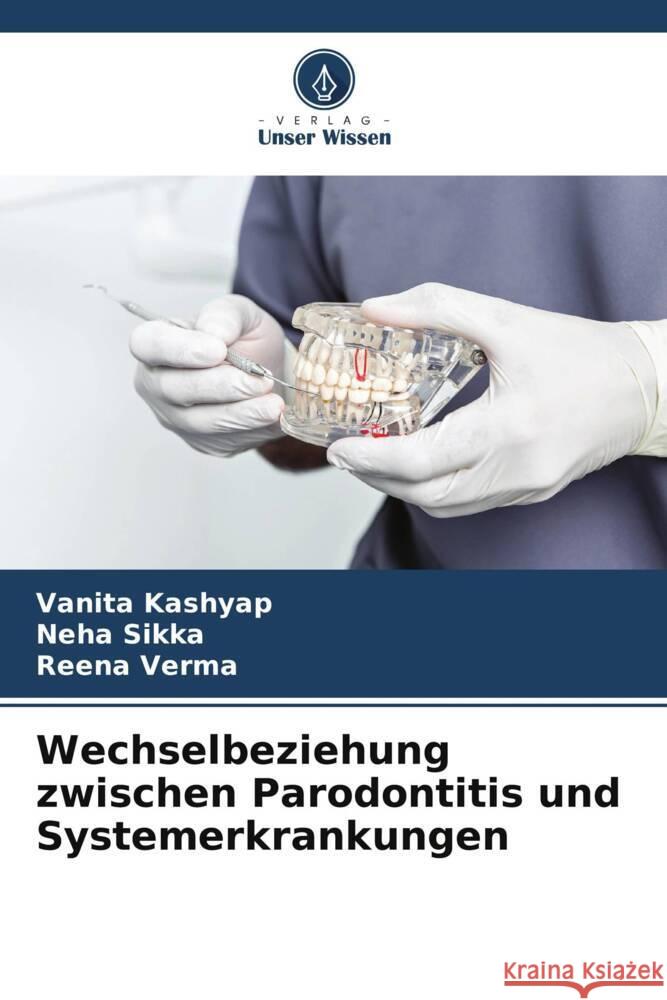 |
Wechselbeziehung zwischen Parodontitis und Systemerkrankungen
ISBN: 9786208321895 / Niemiecki / Miękka / 2024 / 96 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. Die Pathogenese der Parodontitis als Ursache systemischer Erkrankungen ist noch nicht vollständig geklärt. Es ist auch möglich, dass die Parodontitis nicht direkt mit der Verursachung systemischer Erkrankungen zusammenhängt, sondern dass beide gemeinsame Risikofaktoren aufweisen. Zu den umweltbedingten Risikofaktoren und Indikatoren, die Parodontitis und systemische Erkrankungen (wie Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen, Diabetes mellitus, Atemwegserkrankungen, Osteoporose, rheumatoide Arthritis und ungünstige Schwangerschaftsergebnisse) gemeinsam haben, gehören Tabakrauchen, Stress, Alterung,...
Die Pathogenese der Parodontitis als Ursache systemischer Erkrankungen ist noch nicht vollständig geklärt. Es ist auch möglich, dass die Parodontit...
|
cena:
271,70 |
 |
Fluorures et fluorose non squelettique
ISBN: 9786208355487 / Francuski / Miękka / 2024 / 100 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. Les fluorures jouent un rôle central dans la prévention des caries dentaires. Le fluor est ajouté à l'eau potable ou au sel et/ou au lait dans les régions où la fluoration de l'eau n'est pas possible. Ils sont également disponibles sous forme de comprimés et de gouttes en tant que compléments alimentaires pour les enfants. L'utilisation généralisée de ces différents véhicules pour l'administration systémique ou topique de fluorure est sans aucun doute en grande partie responsable du déclin remarquable de la prévalence des caries dentaires. La relation inverse bien établie...
Les fluorures jouent un rôle central dans la prévention des caries dentaires. Le fluor est ajouté à l'eau potable ou au sel et/ou au lait dans les...
|
cena:
275,95 |
 |
Relations entre parodontite et maladies systémiques
ISBN: 9786208321901 / Francuski / Miękka / 2024 / 96 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. La pathogénie de la parodontite dans l'apparition des maladies systémiques est incomplètement comprise. Il est également possible que la parodontite ne soit pas directement liée à la cause des maladies systémiques, mais qu'elles partagent toutes deux des facteurs de risque communs. Parmi les facteurs de risque environnementaux et les indicateurs communs à la parodontite et aux maladies systémiques (telles que les maladies cardiovasculaires, le diabète sucré, les maladies respiratoires, l'ostéoporose, la polyarthrite rhumatoïde et les issues défavorables de la grossesse) figurent...
La pathogénie de la parodontite dans l'apparition des maladies systémiques est incomplètement comprise. Il est également possible que la parodonti...
|
cena:
271,70 |
 |
Interrelazione parodontale e sistemica
ISBN: 9786208321925 / Włoski / Miękka / 2024 / 92 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. |
cena:
271,70 |
 |
Fluoriden en niet-skeletale fluorose
ISBN: 9786208355463 / Holenderski / Miękka / 2024 / 104 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 10-14 dni roboczych. |
cena:
276,87 |
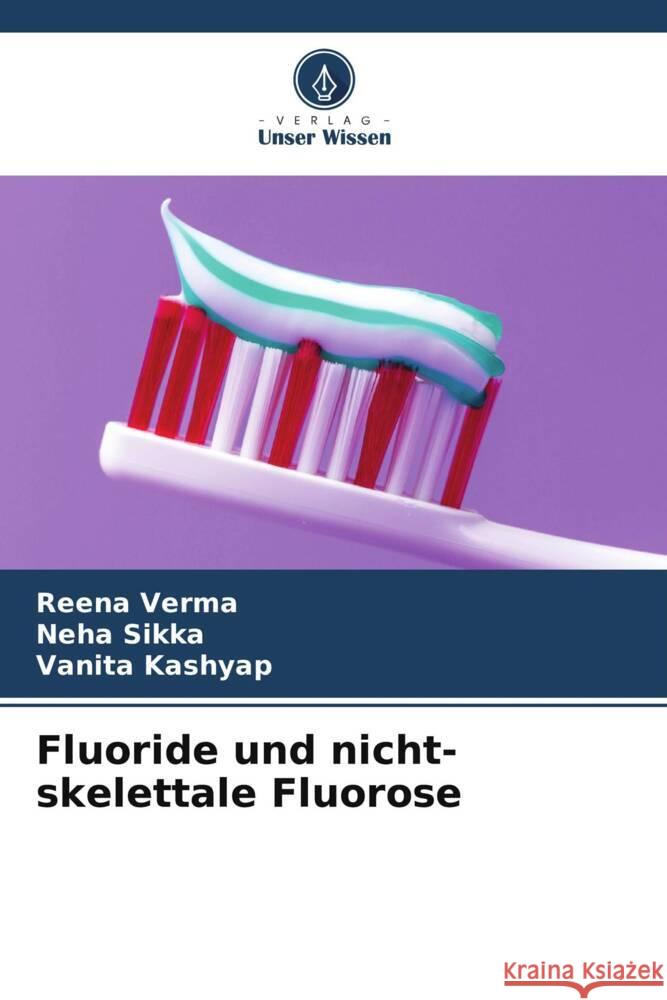 |
Fluoride und nicht-skelettale Fluorose
ISBN: 9786208355470 / Niemiecki / Miękka / 2024 / 108 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 16-18 dni roboczych. Fluoride spielen eine zentrale Rolle bei der Prävention von Zahnkaries. Fluoride werden dem Trinkwasser oder in Regionen, in denen eine Fluoridierung der zentralen Wasserversorgung nicht möglich ist, dem Salz und/oder der Milch zugesetzt. Als Nahrungsergänzungsmittel für Kinder sind sie auch in Form von Tabletten und Tropfen erhältlich. Der weit verbreitete Einsatz dieser verschiedenen Mittel zur systemischen oder topischen Verabreichung von Fluorid ist zweifellos zu einem großen Teil für den bemerkenswerten Rückgang der Kariesprävalenz verantwortlich. Die gut belegte umgekehrte...
Fluoride spielen eine zentrale Rolle bei der Prävention von Zahnkaries. Fluoride werden dem Trinkwasser oder in Regionen, in denen eine Fluoridierung...
|
cena:
275,95 |
 |
Onderling verband tussen parodontitis en systemische aandoeningen
ISBN: 9786208321888 / Holenderski / Miękka / 2024 / 100 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 10-14 dni roboczych. |
cena:
276,87 |
 |
Periodontal and systemic interrelationship
ISBN: 9783659850424 / Angielski / Miękka / 2016 / 152 str. Termin realizacji zamówienia: ok. 10-14 dni roboczych. |
cena:
276,87 |










